7 Types of Organizational Charts (With Examples)
Discover More Helpful Information!
Welcome to EdrawMind!![]() Unleash your creativity and enhance productivity with our intuitive mind mapping software.
Unleash your creativity and enhance productivity with our intuitive mind mapping software.
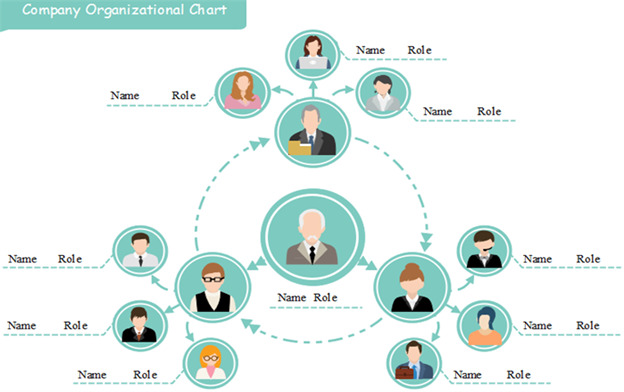
Source: Pngio
For any corporation, organizational charts are essential, strengthening internal processes and supporting connectivity. They will help: improve coordination and collaboration through departments and the broader organization. Boost the exchange of knowledge and teams' flexibility.
There are several varieties of organizational charts, and there are many kinds of administrative systems. Let's go over the seven different forms of org systems and why each one of them should be considered.
Types of Organizational Charts
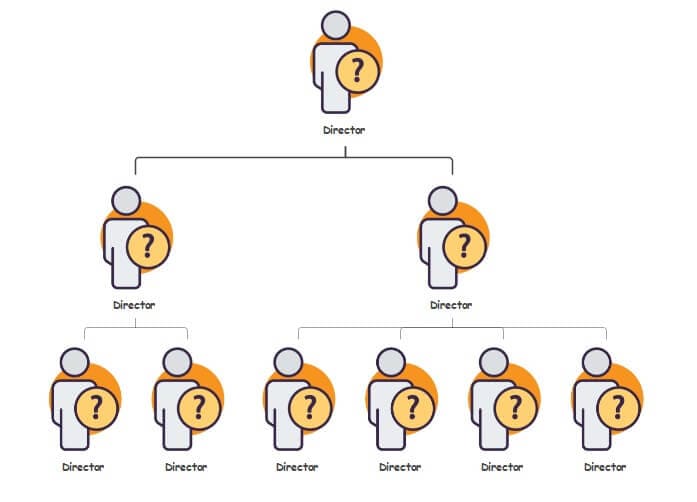
1. Hierarchical org structure
The organizational map that is in the shape of a pyramid is classified as a hierarchical org-chart. It's the most popular corporate type. The axis of influence goes from high to low.
For example,
- The CEO or boss on the Top
- Entry-level and low-level staff
- Each worker has a manager.
Pros
- Better distinguishes jurisdiction and accountability standards
- Indicates who each employee refers to or who to speak to about particular projects;
- Motivates workers with consistent career paths and resources to progress
- Offer a specialization to each employee
- Develop a sense of community between workers of the same unit
Cons
- May slow down progress or make significant adjustments due to additional bureaucracy
- Can lead workers to work for the department rather than for the entire business
- It may make low-level workers feel like they have no control and can't communicate their thoughts to the organization.
2. Functional org structure
Like a hierarchy system, a functional organization structure begins from and moves down roles with the highest degree of obligations on the Top. However, workers are grouped mainly according to their expertise and position within the organization. Each department is separately administered.
Pros
- Enables workers to concentrate on their job
- Encourages experience
- Assistance teams and programs are autonomous.
- It can be scaled effectively in any big business.
Cons
- May build silos in a business.
- Interdepartmental coordination restricts
- Obscures procedures and methods in a business for various markets or goods
3. Horizontal or flat org structure
A horizontal or flat hierarchical arrangement suits industries with few workers at the top employee-management level. Before becoming big enough to create various divisions, many startup firms use a horizontal organ structure. Still, some enterprises keep this structure because it promotes reduced oversight and more significant interaction from all workers.
Pros
- Gives additional responsibilities to workers
- Promotes more transparent interaction
- Enhances teamwork and pace of execution of fresh concepts
Cons
- It may produce uncertainty when workers may not have a specific boss to report to
- Staff members with more straightforward capabilities can be created
- When the organization expands past startup status, it can be hard to manage.
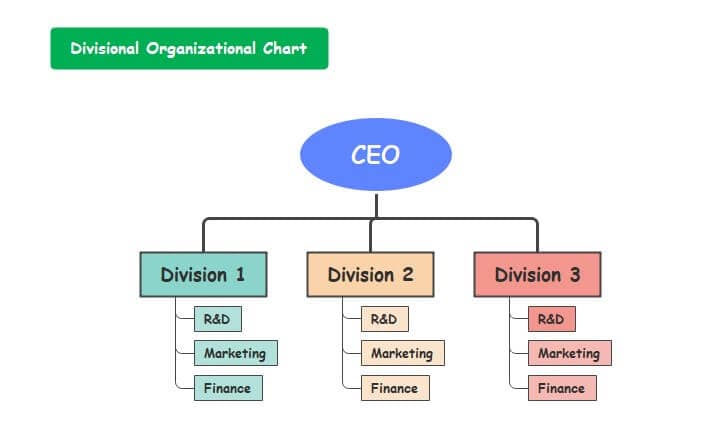
4. Divisional org structure
The divisions within a corporation have power over their personnel in divisional corporate systems, effectively functioning within the broader entity as their own business. Each group can have its specific promotions workforce, distribution team, IT team, etc. For big corporations, this arrangement fits best as it encourages multiple departments to make choices without anyone having to answer to only a few executives.
There are a few variants to note, based on the focus of the company.
- Market-based divisional organizational structure
- Product-based divisional org structure
- Geographic divisional organizational structure
Pros
- Helps major firms stay flexible
- Enables a faster response to developments in the market or consumer needs
- Promotes democracy, freedom, and a personalized strategy
Cons
- Can easily contribute to identical resources
- Muddled or ineffective coordination between the leadership and its departments.
- It can lead to a business fighting with itself.
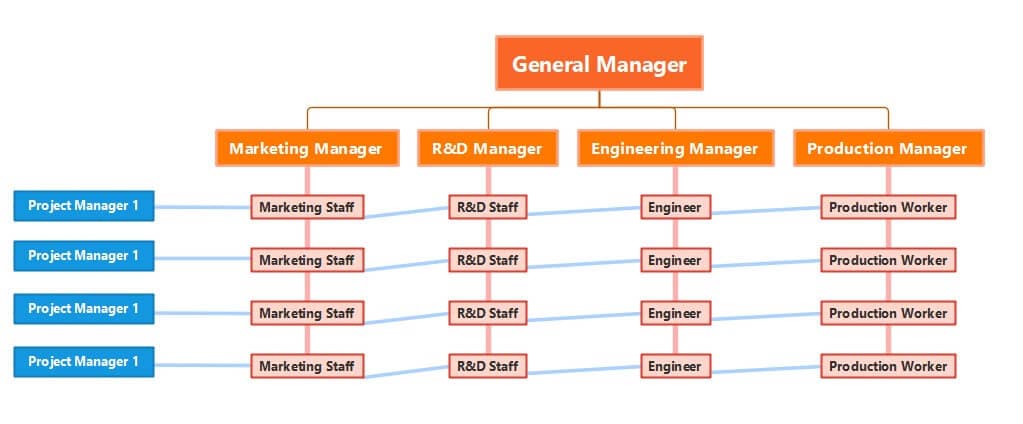
5. Matrix org structure
A map looks like a hierarchical matrix map, and it displays cross-functional teams forming for specific tasks. An engineer can, for example, routinely contribute to the engineering division (led by an engineering manager) but serve on a seasonal job (led by a project manager). For these positions and reporting partnerships, the matrix org map allows for both.
Pros
- Allows managers to pick individuals according to a project's needs quickly
- Gives the enterprise a more dynamic understanding.
- Encourages staff to use their expertise in diverse capacities in addition to their initial positions
Cons
- Introduces a disagreement between the management of departments and project managers
- May change more often than other forms of the organizational map.
6. Team-based org structure
It would come as no mystery that a team-based organizational system divides workers by departments. A team organizational structure is expected to challenge the conventional hierarchy, concentrating more on conflict resolution, teamwork, and giving more autonomy to workers.
Pros
- Increases efficiency, accountability, and openness by cracking down on barriers
- Promotes a mentality of success
- Modifies conventional career styles by encouraging individuals to switch sideways
- Experience of principles instead of seniority
- Needs limited leadership
- Plays best for agile scrum or tiger squad enterprises.
Cons
- Goes against the inherent tendency of specific organizations to a strictly bureaucratic system.
- Might allow promoting pathways less transparent for workers
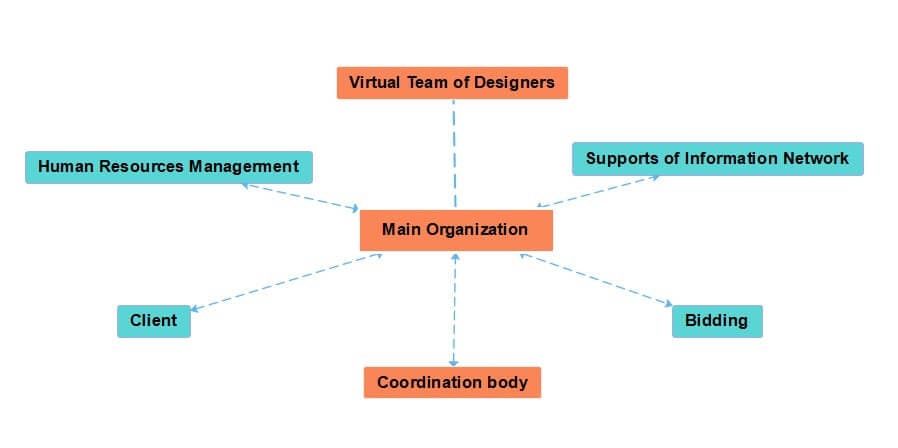
7. Network org structure
Today, few companies have all their resources under one roof, yet managing many suppliers, private contractors, freelancers, off-site places, and regional offices can be overwhelming. The distribution of capital is meaningful in a network organizational system. It may also define an organizational framework that relies more on open communication and connections than on hierarchy.
Pros
- View the complex network of business on-site and off-site links
- Enables enterprises to be versatile and adaptive
- Give all workers the power to work together, take action, and decide.
- Makes workers and customers appreciate procedures and workflows
Cons
- Can be unnecessarily complicated when interacting with specific off-site systems
- It may make it more challenging for workers to know who has the final say.
Conclusion
All kinds of corporations need organizational charts to build their company's framework. That's why they are of vital importance. Every organization has a different setup, so it's vital to understand its interests, business philosophy, and select one of those organizational structures that best suit your organization's culture and division.
MindMaster aims to create innovative visual technologies that help you create organizational charts just according to your demand. MindMaster allows you to sort your creative ideas to find answers to problems. Its built-in templates are straightforward and easy to use. That makes it the top choice for businesses from all across the world.


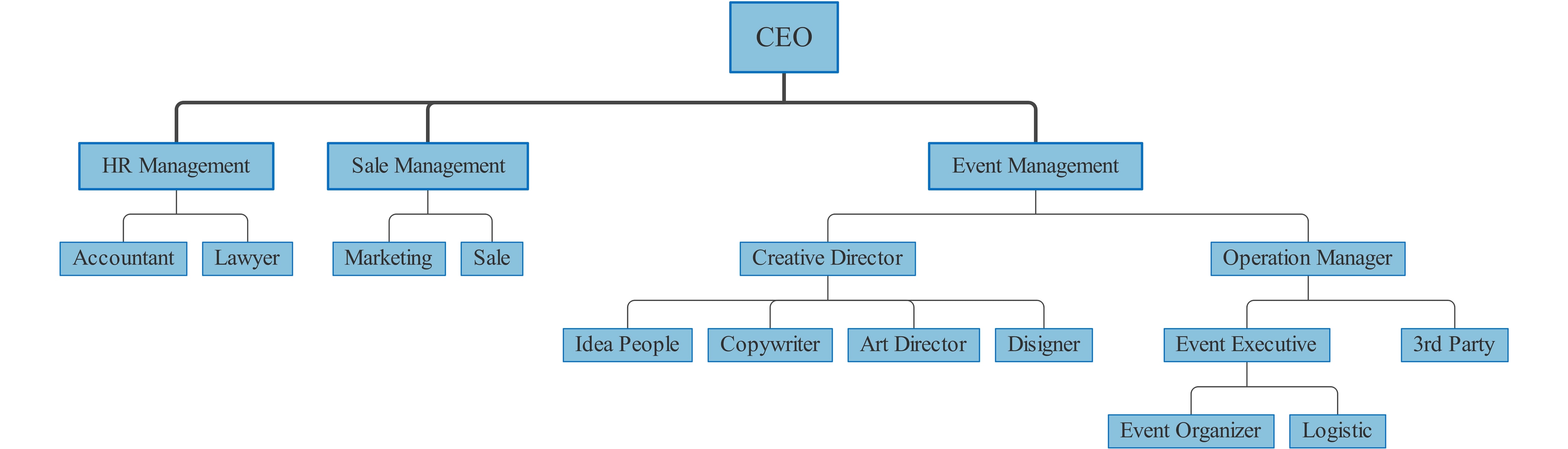

 below.
below.  below.
below.