History of Sweden

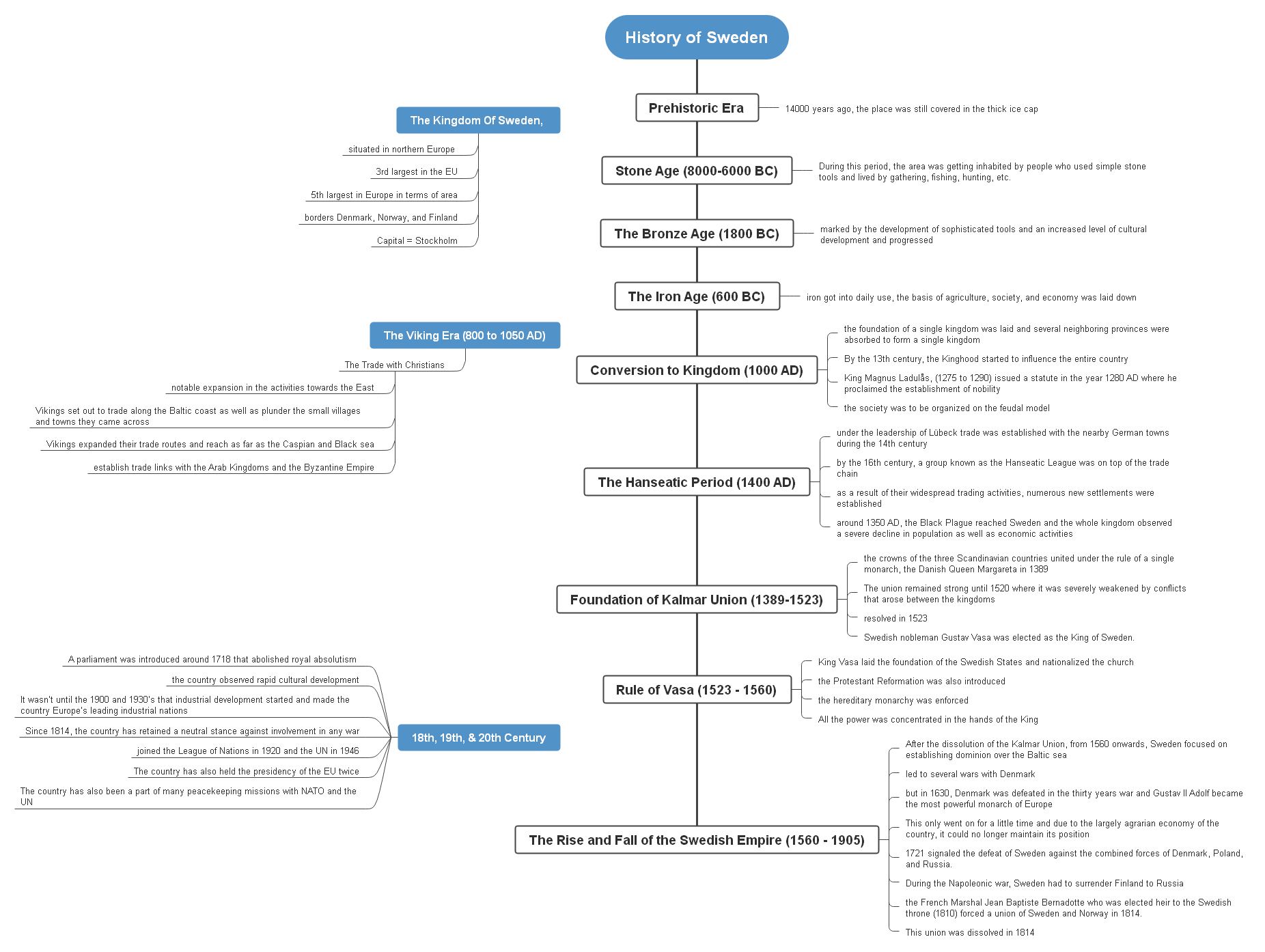
Sweden, or as it is officially known as “The Kingdom of Sweden” is situated in northern Europe as the largest country of the region; 3rd largest in the EU; and the 5th largest in Europe in terms of area. It is a Nordic country that borders Denmark, Norway, and Finland. The capital of the country is Stockholm. Its current population is around 10,099,265.
Sweden has a rich history with Vikings being among a few prominent characters that originated from the region. Additionally, Norse mythology makes Swedish history all the more interesting as there are numerous famous movies (such as Marvel’s Thor) are based around it. But in this piece, we will be having a look at the officially recorded timeline of the country along the course of history with mind maps to help us better understand it.
About 14000 years ago, the place where Sweden is situated is still covered in the thick ice cap. As the snow gave way, people started to move in and make a living for themselves in the harsh and cold environment of the place. This was the time before the wars, and blood-thirsty Vikings rampaged the region.
During this period, the area was getting inhabited by people who used simple stone tools and lived by gathering, fishing, hunting, etc. Ruins and artifacts dating as far back as 1800 BC are still found in the region.
The bronze age in the region started around 1800 BC which was marked by the development of sophisticated tools and an increased level of cultural development and progressed all the way up to 500BC.
The artifacts found associated with the Bronze age started to diminish around 600BC which is when the iron age started. As iron got into daily use, the basis of agriculture, society, and economy was laid down. Sweden was actually starting to get settled.
This era has been marked between 800 to 1050 AD, characterized by a notable expansion in the activities towards the East. The Vikings set out to trade along the Baltic coast as well as plunder the small villages and towns they came across. The region they traded and sailed across forms present-day Russia. The Vikings expanded their trade routes and reach as far as the Caspian and Black sea; where they establish trade links with the Arab Kingdoms and the Byzantine Empire.
Though Sweden converted into a Christian country around the 11 century AD, the teachings of Christ had reached its shores as far back as the 9th century AD in a mission led by Ansgar.
It wasn’t until late 1000 AD that the foundation of a single kingdom was laid and several neighboring provinces were absorbed to form a single kingdom. By the 13th century, the Kinghood started to influence the entire country and the whole kingdom started to fell in place. The King at that time, Magnus Ladulås, who ruled from 1275 to 1290 issued a statute in the year 1280 AD where he proclaimed the establishment of nobility. This meant that the society was to be organized on the feudal model.
It was under the leadership of Lübeck that trade was established with the nearby German towns during the 14th century. But by the 16th century, a group known as the Hanseatic League was on top of the trade chain and as a result of their widespread trading activities, numerous new settlements were established.
Sadly, around 1350 AD, the Black Plague reached Sweden and the whole kingdom observed a severe decline in population as well as economic activities.
With the whole of Europe recovering from the effects of the Black Plague, the crowns of the three Scandinavian countries (Sweden, Denmark, and Norway) united under the rule of a single monarch, the Danish Queen Margareta in 1389 and laid the foundation of Kalmar Union around 1397. The union remained strong until 1520 where it was severely weakened by conflicts that arose between the kingdoms and was finally resolved in 1523. At the end of this, a Swedish nobleman Gustav Vasa was elected as the King of Sweden.
During this period, King Vasa laid the foundation of the Swedish States and nationalized the church with its estates confiscated by the crown. Furthermore, the Protestant Reformation was also introduced, and the hereditary monarchy was enforced. All the power was concentrated in the hands of the King. This was by the year 544.
After the dissolution of the Kalmar Union, from 1560 onwards, Sweden focused on establishing dominion over the Baltic sea. This led to several wars with Denmark; but in 1630, Denmark was defeated in the thirty years war and Gustav II Adolf became the most powerful monarch of Europe. This only went on for a little time and due to the largely agrarian economy of the country, it could no longer maintain its position. 1721 signaled the defeat of Sweden against the combined forces of Denmark, Poland, and Russia.
During the Napoleonic war, Sweden had to surrender Finland to Russia, while the French Marshal Jean Baptiste Bernadotte who was elected heir to the Swedish throne (1810) forced a union of Sweden and Norway in 1814. This union was dissolved in 1814.
A parliament was introduced around 1718 that abolished royal absolutism and the country observed rapid cultural development. It wasn’t until the 1900 and 1930’s that industrial development started and made the country Europe’s leading industrial nations.
Since 1814, the country has retained a neutral stance against involvement in any war. It joined the League of Nations in 1920 and the UN in 1946. The country has also been a part of many peacekeeping missions with NATO and the UN. The country has also held the presidency of the EU twice, first from 1st January to 30th June 2001 and second, 30th June to 31st December 2009.
Though there is still a lot more that could have been mentioned here that would have stagnated this piece with too much information. We hope this piece was an interesting read and the mind maps made it easy to follow through on the entire timeline.