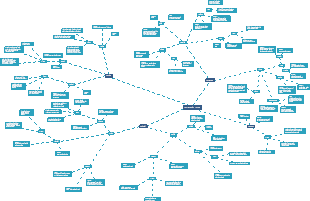
Immediate (Type I) Hypersensitivity
IgE is formed as a result of prior sensitization and coats mast cells and basophils.
Subsequent encounter with antigen results in an IgE-mediated reaction by preformed IgE antibodies (crosslinking)
Release of histamine and other mediators
Mast cell secretion of cytokines and other proinflammatory mediators
eosinophil and neutrophil chemotaxis
late-phase reaction
inflammation and tissue damage
Cytotoxic (Type II) Hypersensitivity
IgM and IgG mistakenly bind to surface antigens of the cells in the body
Cellular Destruction
Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity
Target cell opsonization
Phagocytosis/Complement activation
Inflammation
Fc-receptor mediated immune cell activation
Antibodies bind to cellular surfaces
Subtoactivation of the complement systempic
Impaired cellular function
Antibodies bind to cell surface receptors
Inhibition or activation of downstream signaling pathways
impaired cellular function
Immune Complex-Mediated (Type III) Hypersensitivity
Antigen binds to IgG to form an immune complex (antigen-antibody complex)
Immune complexes are deposited in tissue, especially blood vessels
Initiation of complement cascade
Release of lysosomal enzymes from neutrophils
Cell-mediated (Type IV) Hypersensitivity
T cell sensitization
Skin pentration by the antigen
Uptake of the antigen by Langerhans Cell
Migrastion to lymph nodes
fFrmation of sensitized T lymphocytes
Presensitized T cell response (after repeated contact with the antigen)
CD4+ T cells recognize antigens on antigen-presenting cells
Release of inflammatory lymphokines cytokines
Macrophages activation
Phagocytosis of target cells
CD8+ T cells recognize antigens on somatic cells
cell-mediated cytotoxicity
bronchospasm, abdominal cramping
↑ Smooth muscle contraction
Hypersensitivity l-lv
If not treated:
It prrovides the perfect place for bacteria to accumulate, grow, and cause infection. Untreated allergies may also worsen other chronic problems such as asthma, and skin disorders like eczema and hives.
Cyclophosphamide
- urinalysis
- blood test
- chest x ray
- kidney biopsy
Allergic contact dermatitis
-Gender (Female)
-Concomitant Infections (HIV, Herpes)
-Concurrent Illnesses (Systemic lupus erythematosus)
-Family History
-Age
-Asthma
- Environmental factors (climate, air, pollution)
-Airborne Allergens (pollens, dust, etc)
-Foods (peanuts, wheat, shelffish, etc.)
-Insect stings (bee or wasp)