MindMap Gallery Project quality management
- 8
Project quality management
The mind map of project quality management, including the process of project quality management and how to control quality, is very suitable for people who do quality assurance or take high-level courses.
Edited at 2021-10-28 13:50:13- One Hundred Years of Solitude Character Relationship Chart
One Hundred Years of Solitude is the masterpiece of Gabriel Garcia Marquez. Reading this book begins with making sense of the characters' relationships, which are centered on the Buendía family and tells the story of the family's prosperity and decline, internal relationships and political struggles, self-mixing and rebirth over the course of a hundred years.
- One Hundred Years of Solitude Character Relationship Chart
One Hundred Years of Solitude is the masterpiece of Gabriel Garcia Marquez. Reading this book begins with making sense of the characters' relationships, which are centered on the Buendía family and tells the story of the family's prosperity and decline, internal relationships and political struggles, self-mixing and rebirth over the course of a hundred years.
- Project Management Process Template
Project management is the process of applying specialized knowledge, skills, tools, and methods to project activities so that the project can achieve or exceed the set needs and expectations within the constraints of limited resources. This diagram provides a comprehensive overview of the 8 components of the project management process and can be used as a generic template for direct application.
Project quality management
- One Hundred Years of Solitude Character Relationship Chart
One Hundred Years of Solitude is the masterpiece of Gabriel Garcia Marquez. Reading this book begins with making sense of the characters' relationships, which are centered on the Buendía family and tells the story of the family's prosperity and decline, internal relationships and political struggles, self-mixing and rebirth over the course of a hundred years.
- One Hundred Years of Solitude Character Relationship Chart
One Hundred Years of Solitude is the masterpiece of Gabriel Garcia Marquez. Reading this book begins with making sense of the characters' relationships, which are centered on the Buendía family and tells the story of the family's prosperity and decline, internal relationships and political struggles, self-mixing and rebirth over the course of a hundred years.
- Project Management Process Template
Project management is the process of applying specialized knowledge, skills, tools, and methods to project activities so that the project can achieve or exceed the set needs and expectations within the constraints of limited resources. This diagram provides a comprehensive overview of the 8 components of the project management process and can be used as a generic template for direct application.
- Recommended to you
- Outline
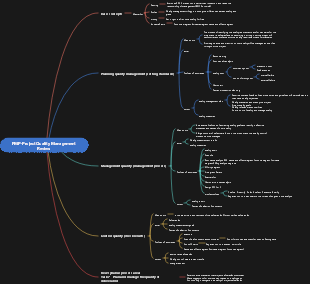
Chapter 8 Project Quality Management
Management guru
Deming PDCA
Shewhart proposed that Deming perfected
14 principles of quality management
keep improve
adopt new ideas
Prevention is better than inspection
85% of quality costs are management issues
...
PDCA
P plan: Set the methods or standards necessary to achieve the goal
D Implementation: Implement specific work step by step as planned
C Confirmation Check: Confirm and check the effect of implementation
Measure A: Confirm the difference between the actual effect and the plan, and take measures as necessary
Juran mass spiral (mass ring)
Emphasis on quality is fitness for use
Propose the difference between quality and grade
Propose a trilogy of quality management: quality planning, quality control, and quality improvement
Crusby Zero Defects
Emphasis on quality as meeting requirements
Emphasize doing things right the first time
Propose quality for free
It is proposed that quality should be measured by non-conformity cost
Ishikawa Fishbone Diagram
Propose quality circle
Summarize the use of the seven quality tools
Taguchi Genichi mass loss function
Propose experimental design methods
Propose robust design methods
Kaizen (improvement); project quality management should take into account both project management and project deliverables
Core idea
Quality, as an achieved performance or outcome, is the degree to which a series of intrinsic characteristics meet requirements.
Levels, as design intent, are level classifications of deliverables that have the same purpose but different technical characteristics.
High quality does not necessarily mean high quality; low grade does not necessarily mean low quality
A quality level that does not meet the quality requirements is definitely a problem, but a low grade is not necessarily a problem
The project manager and the project management team are responsible for the trade-offs to achieve both the required quality and grade levels
Understanding terminology within quality management
prevention
Ensure no errors occur during the process
examine
Ensure that errors do not fall into the hands of customers
attribute sampling
The result is pass or fail
variable sampling
Indicate the degree of qualification
tolerance
acceptable range of results
control limits
Bounds on Ordinary Deviations of Stable Processes
Five levels of quality management in increasing order of effectiveness
1. Let customers discover defects
2. Detect and correct defects through the quality control process before delivering to customers
3. Pass quality assurance checks and correct the process itself
4. Integrate quality into the planning and design of projects and products
5. Create a culture throughout the organization that is focused on and committed to process and product quality.
Project Quality Management Trends and Emerging Practices
Customer satisfaction
Understand, assess, define and manage requirements; meet requirements Suitable for use
keep improve
Continuous small improvements, the PDCA cycle is the basis for quality improvement
Management Responsibilities
85/15 principle
Mutually beneficial relationships with suppliers
interdependence, long-term relationship
Prevention is better than inspection
Quality comes from planning and implementation, not inspection
quality cost
Cost of conforming work (prevention) Cost of non-conforming work (correction)
against gilding
Gold plating will cause greater opportunity costs
Get it right the first time, quality is free
Zero defect management
Just-in-time (zero inventory) management
Strive to do it right the first time and strive for zero defects
total quality management
Emphasis on quality management throughout the entire process and participation of all employees
Factors to consider when cutting
Policy Compliance and Audit
Standard syntax compliance
keep improve
Stakeholder participation
Agile and adaptive environment considerations
Changes are implemented throughout the entire project rather than at the end
Cycle review and regularly check the results
Find the cause of the problem and suggest ways to improve it
Evaluate the test process and determine measures
Focus on small batch jobs
Control Quality (Monitoring Process Group) Check Results
Concept and function
The process of monitoring and documenting quality management to drive execution results in order to evaluate performance and ensure that project outputs are complete, correct, and meet customer expectations.
However, the project deliverables and work have met the requirements of the major stakeholders and are ready for final acceptance.
Quality control should be performed throughout the project
enter
project management plan
quality management plan
project files
Lessons Learned Register
quality measures
Describe project or product attributes and verify compliance
Test and Evaluation Documents
Evaluate the extent to which quality objectives are achieved
Approved change request
Deliverables
Direct and manage the output of project work
job performance data
business environment factors
organizational process assets
Tools & Techniques
data collection
Checklist
Helps manage and control quality activities in a structured manner
checklist
Arrange items appropriately to collect useful data on potential quality issues
statistical sampling
Select samples and determine during planning quality management process
Attribute sampling (pass or fail)
Variable sampling (level of qualification)
Questionnaire
Used to collect data on customer satisfaction after a product or service has been deployed
data analysis
performance review
Measure, compare and analyze quality metrics
Root Cause Analysis
Identify root causes of defects
examine
Inspect whether written standards are met and confirm the number of defects to be compensated
Testing and Product Evaluation
Organized, structured investigation
Data performance
cause and effect diagram
Control Charts
Determine whether the process is stable and has predictable performance
Upper limit of specification, lower limit of specification
upper control limit, lower control limit
tolerance
Histogram
Scatter plot
Meeting
output
Quality test measurement results
Verified deliverables
job performance information
change request
Project Management Plan Update
quality management plan
Project file updates
Problem log
Lessons Learned Register
risk register
Test and Evaluation Documents
Manage Quality (Executive Process Group) Management Process
Concept and function
The process of applying the organization's quality policy to projects and converting the quality management plan into executable quality activities
Increase the likelihood of achieving quality goals, identify ineffective processes, and identify causes of poor quality
The work of managing quality belongs to the consistency work in the quality cost framework
Quality management is sometimes also called quality assurance, the former is broader
People and roles in managing quality
QA department
Full responsibility
In an agile project, all team members execute
enter
project management plan
quality management plan
project files
Lessons Learned Register
Early experience can be used in later stages to improve management efficiency and effectiveness.
Quality control measurement results
Analyze and evaluate whether quality meets standards or requirements and determine the degree of accuracy
quality measures
Set test scenarios and deliverables
risk report
Identify sources of overall project risk and the most important drivers of risk exposure
organizational process assets
Tools & Techniques
data collection
Checklist
A structured tool that lists specific components
data analysis
Alternatives analysis
Choose the most appropriate quality program or method
process analysis
Identify process improvement opportunities
File analysis
Analyze the files output by the project control process to find processes that are out of control and have problems
Root Cause Analysis
Find the root cause and prevent the problem from happening again
decision making
Multi-criteria decision analysis
Discuss alternatives that impact project or product quality
Data performance
Affinity diagram
cause and effect diagram
Fishbone diagram, Ishikawa diagram, why-why analysis diagram, 5 whys
flow chart
Improve processes, identify potential defects, estimate quality costs, and predict error links
Histogram
Central tendency, degree of dispersion, distribution form, frequency of occurrence of specific variables
Matrix diagram
Relationship strength
Scatter plot
Two variables, regression line, strong correlation, independent variable and dependent variable
Pareto chart
Main reasons, 28/20 rule, prioritization, focused corrective measures
audit
A structured, independent process used to determine whether project activities comply with organizational and project policies, processes, and procedures.
Identify and share good and best practices
Identify violations and deficiencies and prepare a defect list
Process improvement, increased productivity, reduced quality costs
Accumulate experience and lessons
Confirm implementation of approved change requests
Design for X
Technical guidance, optimized design, control or improve final product characteristics
problem solved
Discover solutions to problems or challenges
quality improvement methods
PDCA, six sigma
output
quality report
Quality issues, improvement suggestions, corrective action suggestions, situation overview
Test and Evaluation Documents
Evaluate achievement of quality objectives
change request
Suggestions for improvements, corrective actions leading to change requests
Project Management Plan Update
quality management plan
Scope Baseline
progress baseline
cost basis
Project file updates
Problem log
Lessons Learned Register
risk register
Planning Quality Management (Planning Process Group) Setting Standards
Concept and function
The process of identifying the quality requirements and/or standards for the project and its deliverables and describing in writing how the project will demonstrate compliance with the quality requirements and/or standards.
Provide guidance and direction on how quality is managed and verified throughout the project
enter
Project Charter
project management plan
demand management plan
risk management plan
Stakeholder Engagement Plan
Scope Baseline
project files
Hypothetical log
requirements document
Requirements Tracking Matrix
risk register
Interested Party Register
Business environment factors
organizational process assets
Develop project quality policy
Tools & Techniques
expert judgment
data collection
Benchmarking
Identify best practices, formulate suggestions for improvement, and provide basis for performance appraisal
Brainstorming
Emphasis on quantity rather than quality
Interview
Stakeholders and subject matter experts, tacit and explicit, formal and informal, trust and confidentiality environments
data analysis
Cost-benefit analysis
Reduce rework, increase productivity, reduce costs, improve satisfaction, and improve profitability
Compare possibilities with expected benefits
quality cost
consistency cost
prevention cost
Evaluation cost
non-conformity cost
internal failure costs
external failure costs
decision making
Multi-criteria decision analysis
priority matrix
Data performance
flow chart
Improve processes and identify areas where quality defects may occur
SIPOC model
a type of value chain
logical data model
Matrix diagram
Rows and columns cross to show the strength of factor relationships
mind Mapping
Test and inspection planning
Meeting
output
quality management plan
Quality policy, quality standards, quality objectives, roles and responsibilities, related activities, quality tools, etc.
quality measures
Describe the item or product attributes and how the control quality process will verify compliance
Project Management Plan Update
risk management plan
Scope Baseline
Project file updates
Lessons Learned Register
Requirements Tracking Matrix
risk register
Interested Party Register